Role of Geo-Spatial Technology (GIS) in Water Resource Management
INTRODUCTION
Water availability is a critical issue in India, where many regions experience water scarcity and drought. Current research on water availability in India focuses on identifying areas of water stress and developing strategies to manage water resources more effectively. The implementation of advanced geospatial technology has made water resource management activities easier. It includes various water-related data collection, data storage, management, and analysis. IGiS, an indigenous technology, jointly developed by SGL and SAC, ISRO, provides valuable insights for efficient decision-making activities and helps to implement better water management policies through various geospatial analyses for sustainable water resource management.
IGiS provides a robust set of tools for data editing, manipulation, and processing, using advanced drawing and analysis tools. These are beneficial for mapping the water resources, and assets, monitoring water availability, and water quality, identifying potential zones of groundwater, water supply system management, and analyzing the impact of human activities on water resources effectively and efficiently. The Enterprise-based solution of IGiS empowers decision-makers to make enhanced strategies for water management proficiently and with ease.
There are numerous approaches to sustainable water resource management that can be achieved by using IGiS, an integrated GIS and Remote Sensing Platform. Following is a brief discussion of a few applications in the same field:
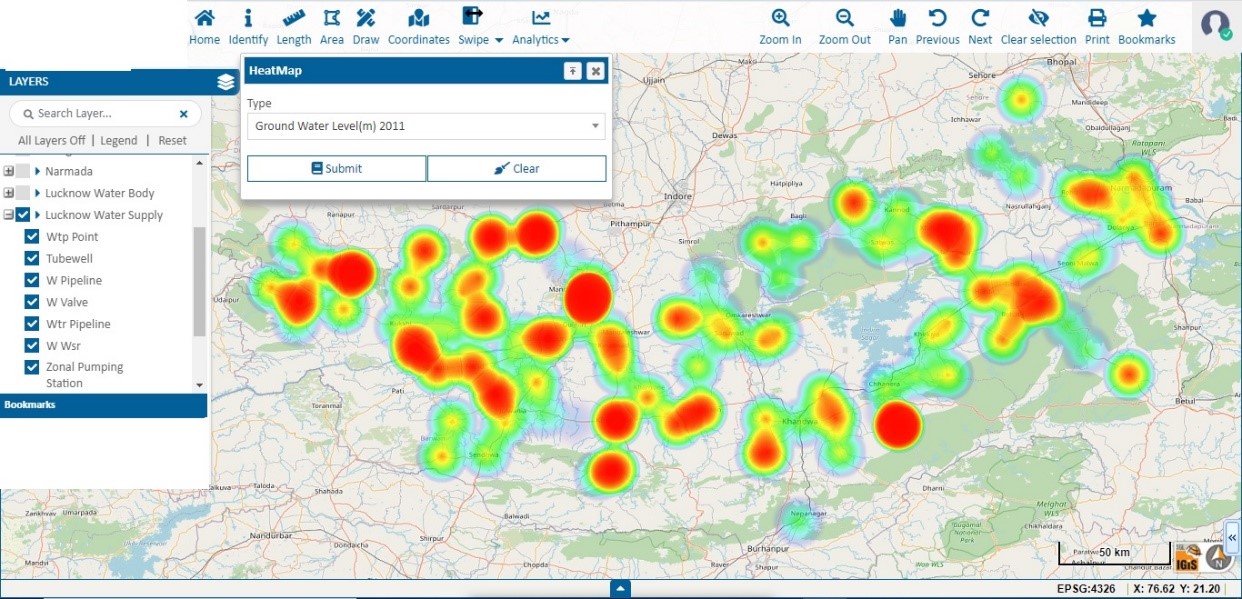
- Ground Water Management
Geographic Information System (GIS) applications are making a major impact on groundwater management in several ways, such as mapping and tracking India’s groundwater resources, including aquifer recharge and depletion rates, water quality, and well locations. Groundwater is an essential source of irrigation, drinking water, and industrial water, but it is often overused in certain regions. IGiS can be used to monitor and inspect water resources through comprehensive maps of groundwater resources, taking into account aquifer boundaries, water levels, and quality information which comes from remotely sensed images and sensors installed in the field. The platform incorporates diverse image-processing techniques that facilitate the identification of potential groundwater zones. It also enables the solution for how groundwater levels will respond when there are changes in rainfall amounts, pumping rates, or other factors. Thus, the integration of GIS technology in the groundwater management system, enhances decision-making, promotes conservation efforts, and facilitates sustainable use of this vital resource.
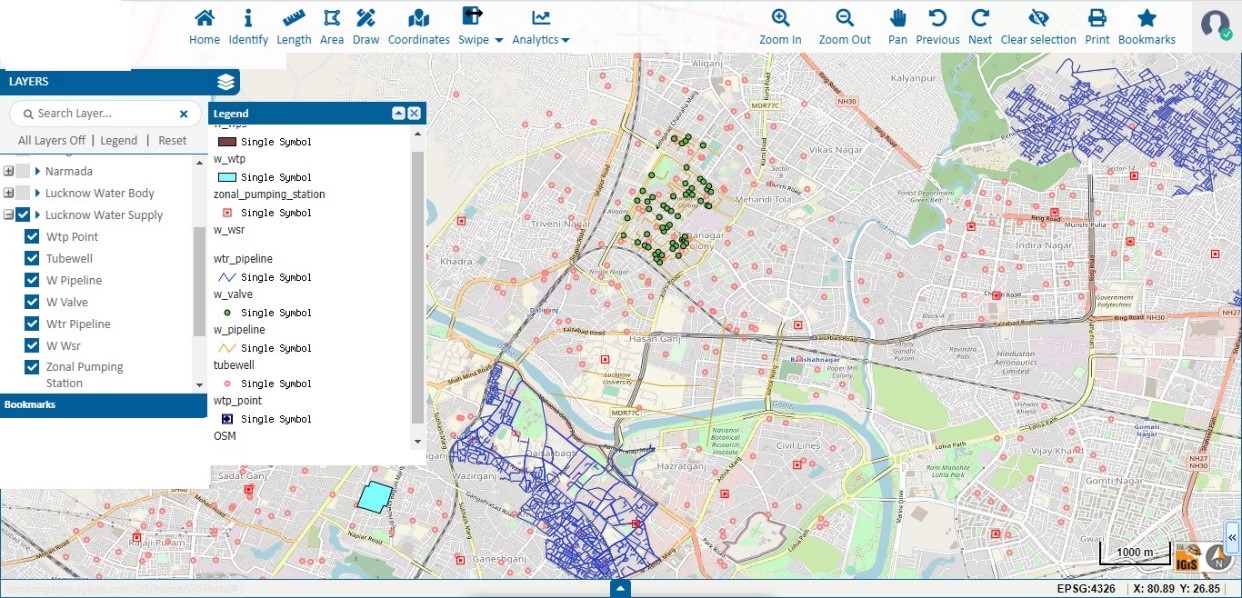
- Water Supply Management
GIS (Geographic Information System) is an essential tool for managing water supplies, as it helps to visualize and assess spatial data related to water resources. This includes creating detailed maps of water treatment plants, reservoirs, pipelines, and distribution networks, assessing population density, and other useful data. With IGiS, authorities can monitor the performance of the entire water system, identify areas with high demand or potential leakage, and decide on the best locations for new infrastructure. Additionally, IGiS can be used to analyse water supply scenarios like the demand for water in a particular area for giving insight to develop effective strategies for managing water sources. Ultimately, IGiS plays a major role in ensuring the sustainable management of water resources.
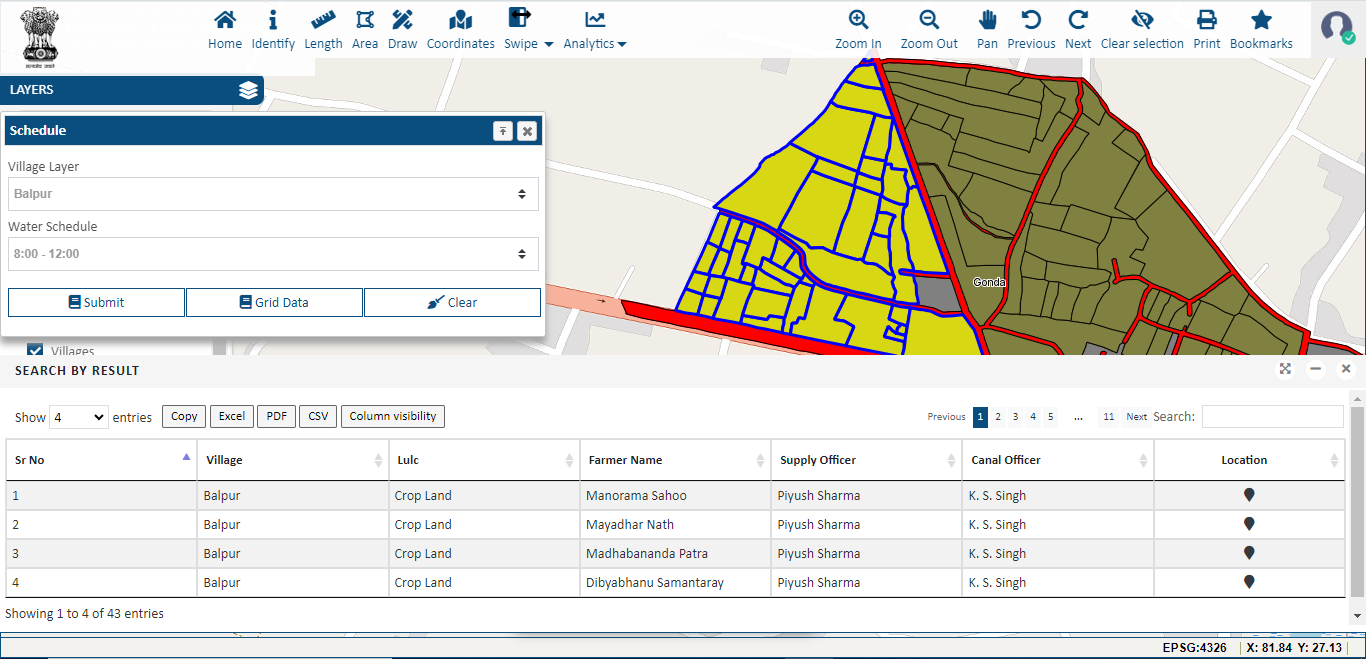
- Water Resource Management for Agriculture
GIS can be highly beneficial in agricultural water resource management. It facilitates the gathering and examination of data related to water sources, such as streams, rivers, and lakes, as well as irrigation systems and soil moisture. This information can be used to enhance water utilization, spot likely water stress areas, and construct irrigation plans. With the help of IGiS, users can also monitor the effect of water usage on crops, soil, and surrounding ecosystems. Additionally, it can facilitate the creation of maps and models to gain knowledge of water movement and availability and identify regions that may necessitate additional water management actions. It also enables the integration of national crop advisory information within the system, to ensure nationwide effectiveness in agriculture. Ultimately, it can be employed to visualize crops, soil types, and water accessibility in agricultural locations for optimizing irrigation procedures and the production of drought-resistant crop varieties.

- Watershed Management
A watershed is an area of land where all the water that falls within it, drains into a common water body, such as a river, lake, or ocean. Watershed management is required to identify the natural flow and the availability of the water and its relation with other factors, like water quality, land use, and vegetation cover for sustainable management of water resources.
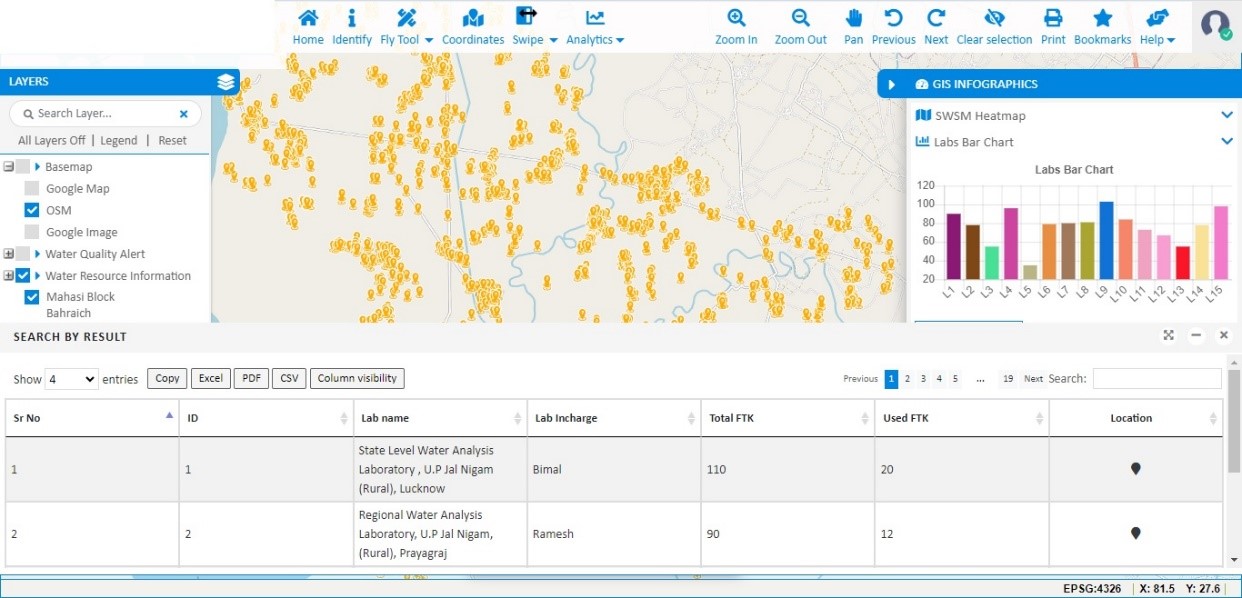
IGiS has the competency of watershed extraction from any Digital Elevation Model. Additionally, it also considers various other factors, such as topography, land use, vegetation cover, soil types, hydrology, and water quality for various advanced analyses. This information can help to identify areas that are particularly vulnerable to erosion, flooding, or pollution and develop strategies to mitigate these issues. Furthermore, IGiS can assist in creating maps and information visualization through various interactive charts and graphs that can help to convey complex information to stakeholders and the public, facilitating their participation in watershed management.
- Water Quality Monitoring:
GIS-based water quality monitoring involves the real-time quality monitoring of various water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs, etc. It helps in understanding the spatial distribution of water quality parameters, identifying pollution sources, and implementing effective management strategies. Real-time water quality monitoring is required to ensure that all humankind and living creatures use safe water in their day-to-day life. Therefore, Internet of Things (IoT) based monitoring systems are used for constant monitoring of the water quality.
Data collected from the IoT Sensors integrate with the GIS-based system for continuous monitoring of the information over the map. The GIS system is also capable of generating alarms when any abnormal changes are found. This information is vital for decision-making related to water quality management, such as selecting appropriate pollution control measures, identifying priority areas for water quality improvement, and assessing the effectiveness of water quality management programs. IGiS allows for the integration of various data sources, such as water quality monitoring data, land use data, and hydrologic data, to create a comprehensive understanding of water quality conditions in a particular area. With IGiS, it is possible to identify the sources and causes of water pollution and visualize the spatial distribution of water quality parameters. Overall, IGiS applications in water quality management help to improve the understanding and management of water resources, ultimately leading to better protection and preservation of water quality for the benefit of people and the environment.
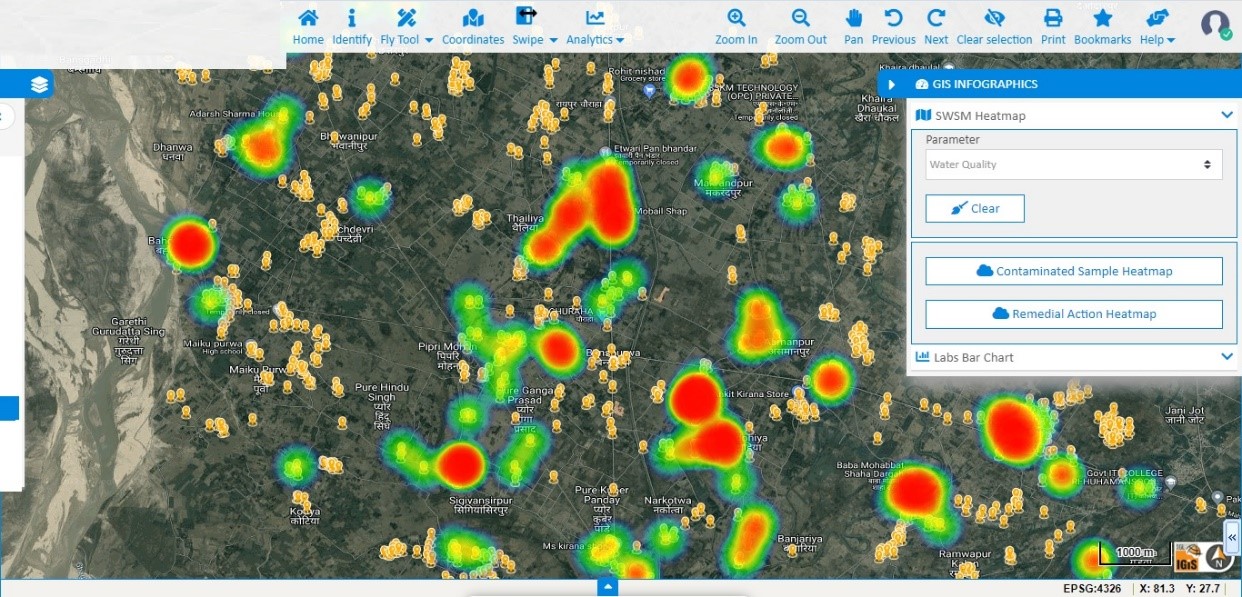
- Infrastructure Management:
Management of the infrastructure is essential for ensuring a continuous water supply. Implementation of GIS in Infrastructure Management can be used to model the impact of population growth and other factors on water demand and infrastructure needs. IGiS allows for accurate mapping and management of water supply and wastewater infrastructure, including pipes, treatment plants, reservoirs, and distribution networks. By digitizing and visualizing this infrastructure data, it becomes easier to identify areas of concern, detect leaks, optimize maintenance schedules, and plan for necessary repairs or upgrades. IGiS also allows the integration of real-time data from sensors and monitoring devices, enhancing the ability to respond promptly to any issues or disruptions in the water supply. This valuable information aids in optimizing the operation and maintenance of these systems, minimizing leaks and water losses, and strategically planning for future infrastructure demands. Moreover, the Multi-criterion decision-making tool in IGiS allows for a comprehensive assessment of different criteria or factors involved in the site selection process such as rainfall patterns, topography, soil type, land use, and proximity to water sources. By considering multiple criteria simultaneously, the tool helps in evaluating and ranking potential sites based on their suitability for Rain Water Harvesting.
CONCLUSION
Water resource management is becoming an increasingly important part of our lives and GIS technology offers us a powerful tool for managing our water resources. With GIS technology, detailed analyses can be done to manage water resources effectively by acquiring more accurate information about water availability, water quality, water depth, etc.
By leveraging the power of IGiS, the cost of water management, the efficiency of water distribution systems, and making smarter decisions about how protecting water resources for future generations may be efficiently addressed. With IGiS, water resource management can be done wisely, and sustainably. So let us take advantage of this technology and use it to preserve our most valuable resource.
Latest Blog

Smart Waste Management with GIS
1. Introduction: Waste management entails the responsible collection, processing, and disposal of waste materials with a focus on environmental preservation. Its core objectives include waste reduction, resource recovery, and the....
Read More